Over the last decade, the field of neuroscience has seen great advancements. Multiple efforts, both public and private, are underway to develop new tools to deepen our understanding of the brain and to create novel technologies that can record, decode, and sense brain signals as well as stimulate, modify, and augment brain function with improved efficacy and safety.
Although current research into and early deployment of neurotechnologies has predominantly focused on medical and therapeutic uses, there are already examples pointing to the push for the commercialization of these technologies for other applications, such as wellness, education, or gaming. As part of our effort to support the neuroengineering community, the IEEE Brain Neuroethics Subcommittee is developing a neuroethical framework for evaluating the ethical, legal, social, and cultural issues that may arise with the deployment of such neurotechnologies. The IEEE Brain neuroethical framework is organized as a matrix of specific types of contemporary neurotechnologies and their current and potential applications.
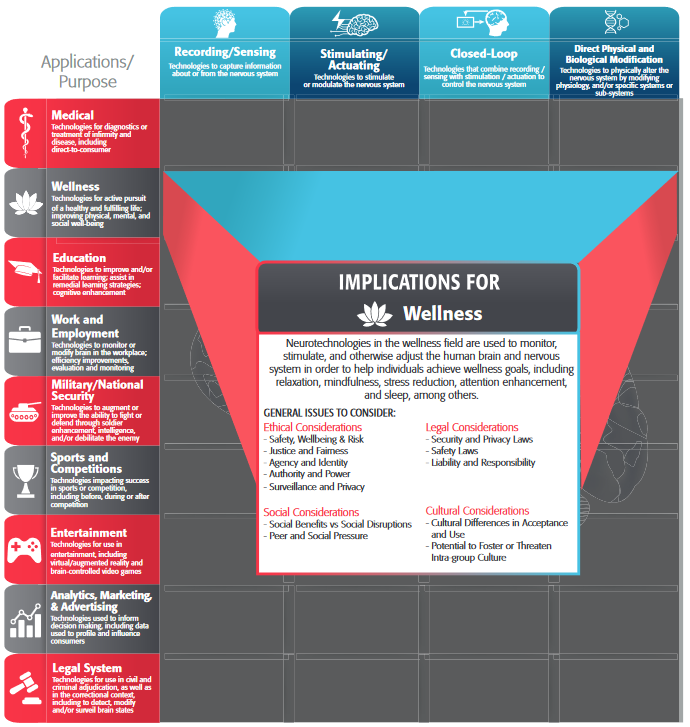
In this framework, we explore the ethical, legal, social, and cultural issues (ELSCI) that are generated by different types of neurotechnologies when used in specific applications. Key areas identified for potential neurotechnology implementation include medicine, wellness, education, work and employment, military and national security, sports and competitions, entertainment, the legal system, as well as marketing and advertising.
We recognize that neurotechnologies are constantly changing, both in terms of the translational pathway and the scope of applications for which they are used. A given neurotechnology might not flourish for a given application but may be used in ways not originally intended. Similarly, the ELSCI of a given device might change based on the particular social context and culture at hand. Accordingly, this framework is intended to serve as a living document, such that the themes and principles only capture a particular moment in time and will need to be revised as neuroscience, neurotechnologies, and their uses evolve. Furthermore, it is intended to facilitate further discussion by inviting input and new perspectives from a wide range of individuals with an interest in neurotechnologies.
While the focus is primarily on current technologies, we discuss potential risks and benefits of technologies for which only limited data is available. Our hope is for the proliferation of research in this field, and we look forward to issuing supplementary resources. Finally, while we acknowledge that there are different ways in which neurotechnologies can be conceptualized, here we focus on neurotechnologies as devices or physical modifications that interface with the human body, supplement pharmaceutical interventions, or that integrate with pharmaceutical agents. We focus on those interventions that use electricity, magnetic pulses, light, or other non-pharmacological agents to bring about their goal. In some cases, these techniques may incorporate genetic modification to the target tissue; however, pure gene therapies that do not involve an associated electronic device are outside the scope of this document.
Each application begins by defining the use case. Next, it identifies and describes existing key examples of the use of neurotechnology in the relevant application area as well as both near-term and long-term applications and the technologies that will enable them. After examining the ethical, legal, social, and cultural considerations for neurotechnologies in that given application, we highlight some examples of regulatory considerations, relevant standards, and a few case studies.
The documentation that supports this framework is the result of ongoing collaboration and dialogue among teams of engineers, scientists, clinicians, ethicists, sociologists, lawyers, and other stakeholders. This document has set the foundation for the ongoing development of socio-technical standards with a focus on neurotechnology (IEEE SA P7700) for engineers, researchers, applied scientists, practitioners, and neurotechnology companies that will help ensure the responsible development and use of new neurotechnologies. This framework will also be of interest to a wide range of audiences and stakeholders interested in neuroethics and the ethical, legal, social, and cultural implications (ELSCI) of these emerging technologies.